How to Create a SQL Statement
Last Updated: October 13, 2022 1:43:00 PM PDT
Give feedback
Use this guide to review how to create a select SQL statement to use in the SQL Executer.
As you review the statements and clauses below, note that brackets identify optional information.Include a bracketed item if you want to select more specific data.
- For helpful hints and problem solutions, SQL Review and Troubleshooting.
Note: If you don't know the SQL programming language, you can use QueryLink by clicking the Queries button in FinancialLink, EmployeeLink, Student/ Class Info tools, and DataLink.
1. Start your query with the select statement.
- select [all | distinct]
A select statement queries the database and retrieves selected data that match the specified criteria.
2. Add field names you want to display.
- field1 [,field2, 3, 4, etc.]
The field name specifies the particular fields that contain the data.Note: You can find field and data table names in the Data Models section of DataLink.
3. Add your statement clause(s) or selection criteria.
- Required:
- from table1[, table2]
The from clause specifies the table(s) that contain the data.
- from table1[, table2]
- where conditions
The where clause specifies the selection condition(s) by which data is retrieved. - order by [column-list]
The order by clause specifies the ordering or sorting of rows. - group by [column-list]
The group by clause groups the resulting rows in sets. - having conditions
The having clause allows a search condition and is used with the group by clause.
4. Review your select statement.
- Here's a sample statement:
select [all | distinct] field1[,field2]
from table1[,table2]
[where conditions]
[group by field-list]
[having conditions]
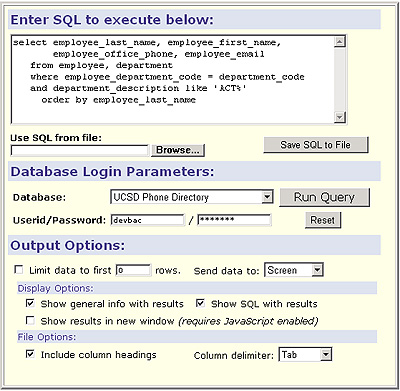
[order by field-list] - The example below shows SQL being used in the SQL Executer to produce a phone list of all ACT staff by last name.
- The list will show last names, first names, phone extensions, and e-mail addresses.
Contact the Data Warehouse team or enroll in a SQL training class.