Radiation Survey: Procedures
Learn how to perform and document a routine radiation survey.
Requirement
Routine surveys are required to detect incidental radiation contamination that may occur during research activities.
- Read Radiation Contamination Survey Overview to determine the appropriate survey method for your lab.
Document lab surveys.
Keep survey documents where they can be easily retrieved upon request by inspectors.
How to perform a meter (direct) survey.

Radiation survey using a meter and probe.
Survey the benchtop, equipment, and inventory and waste storage areas. Check clothing, hands, shoes, regular trash, and the work area floor.
Note: Do not use this method for tritium. Use the wipe test method instead.
- Check the meter's battery condition, then set the range.
- Meters will detect some background radiation, so take a background reading in a clean area before every meter survey.
- Hold the probe within 1/2 inch of the surface. Sweep the area or item at a rate of 1 to 2 inches per second.
- Readings statically different than background indicate contamination.
How to perform a wipe test (indirect) survey.
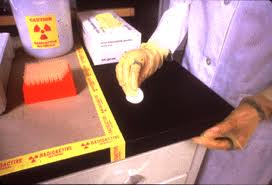
Radiation survey using wipes.
Take enough wipe samples to confidently survey the radioactive materials use area, including the benchtop, equipment, floor, and inventory and waste storage areas.
- Use the wipe test method:
- If you use tritium
- In areas where contamination is detected with a meter
- In areas where meter monitoring is impractical (inside a microfuge, for example)
- In areas where very small amounts of activity are used (less than 1 microcurie)
- To detect background radiation, set up a clean filter or cloth wipe as a blank.
- Using filter paper or cloth wipes, wipe an area of 16 square inches (100 square centimeters) for each sample.
- Analyze the samples using a liquid scintillation counter or gamma counter.
- Areas with readings exceeding these values (in dpm/100 sq cm) are contaminated:
Areas with readings exceeding these values (in dpm/100 sq cm) are contaminated Emission Example isotopes Loose Beta C-14, P-32, P-33, S-35 1,000 Photon Ca-45, Cr-51, Mn-54, 1,000 Photon I-125, I-131 200 Alpha Pb-210, Ra-228 20 Various U-nat, U-dep, Th-nat 200
Clean up contamination.
- Clean up contaminated areas. See How to Clean Up Minor Radioactive Contamination.
- Re-survey using the appropriate method(s) outlined above.
Notice: Refer to the Radiation Safety Manual (PDF) for a detailed description of the UC San Diego radiation safety program.